Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Support Vector Regression for 3D Surface Fitting
This script demonstrates the use of Support Vector Regression (SVR) to model and predict a synthetic 3D surface. The objective is to train the model to approximate the surface defined by the equation:
Z = 2 * X^2 - 5 * Y^2 + noise
The script performs the following steps:
Generates a synthetic 3D dataset with two input features (X, Y) and one output (Z).
Splits the dataset into training and test sets.
Trains an SVR model with a linear kernel (product of two linear kernels) and compares its predictions against a Scikit-learn SVR model with a radial basis function (RBF) kernel.
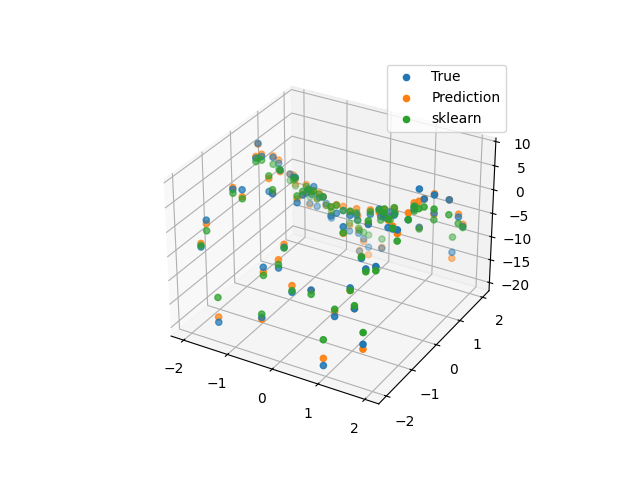
Visualizes the true values and the predictions from both models in a 3D scatter plot.
The comparison allows an evaluation of the model’s performance in approximating the underlying surface.
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm
from DLL.MachineLearning.SupervisedLearning.SupportVectorMachines import SVR
from DLL.Data.Preprocessing import data_split
from DLL.MachineLearning.SupervisedLearning.Kernels import Linear
torch.manual_seed(10)
x = torch.linspace(-2, 2, 20)
y = torch.linspace(-2, 2, 20)
XX, YY = torch.meshgrid(x, y, indexing="xy")
X = XX.flatten()
Y = YY.flatten()
X_input = torch.stack((X, Y), dim=1)
Z = 2 * X ** 2 - 5 * Y ** 2 + torch.normal(0, 1, size=X.size())
x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test, _, _ = data_split(X_input, Z, train_split=0.8, validation_split=0.2)
model = SVR(kernel=Linear() ** 2)
# model = SVR()
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(x_test)
correct = svm.SVR(kernel="rbf", C=1)
correct.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred_true = correct.predict(x_test)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(x_test[:, 0].numpy(), x_test[:, 1].numpy(), y_test.numpy(), label="True")
ax.scatter(x_test[:, 0].numpy(), x_test[:, 1].numpy(), y_pred.numpy(), label="Prediction")
ax.scatter(x_test[:, 0].numpy(), x_test[:, 1].numpy(), y_pred_true, label="sklearn")
ax.legend()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 4.356 seconds)