Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
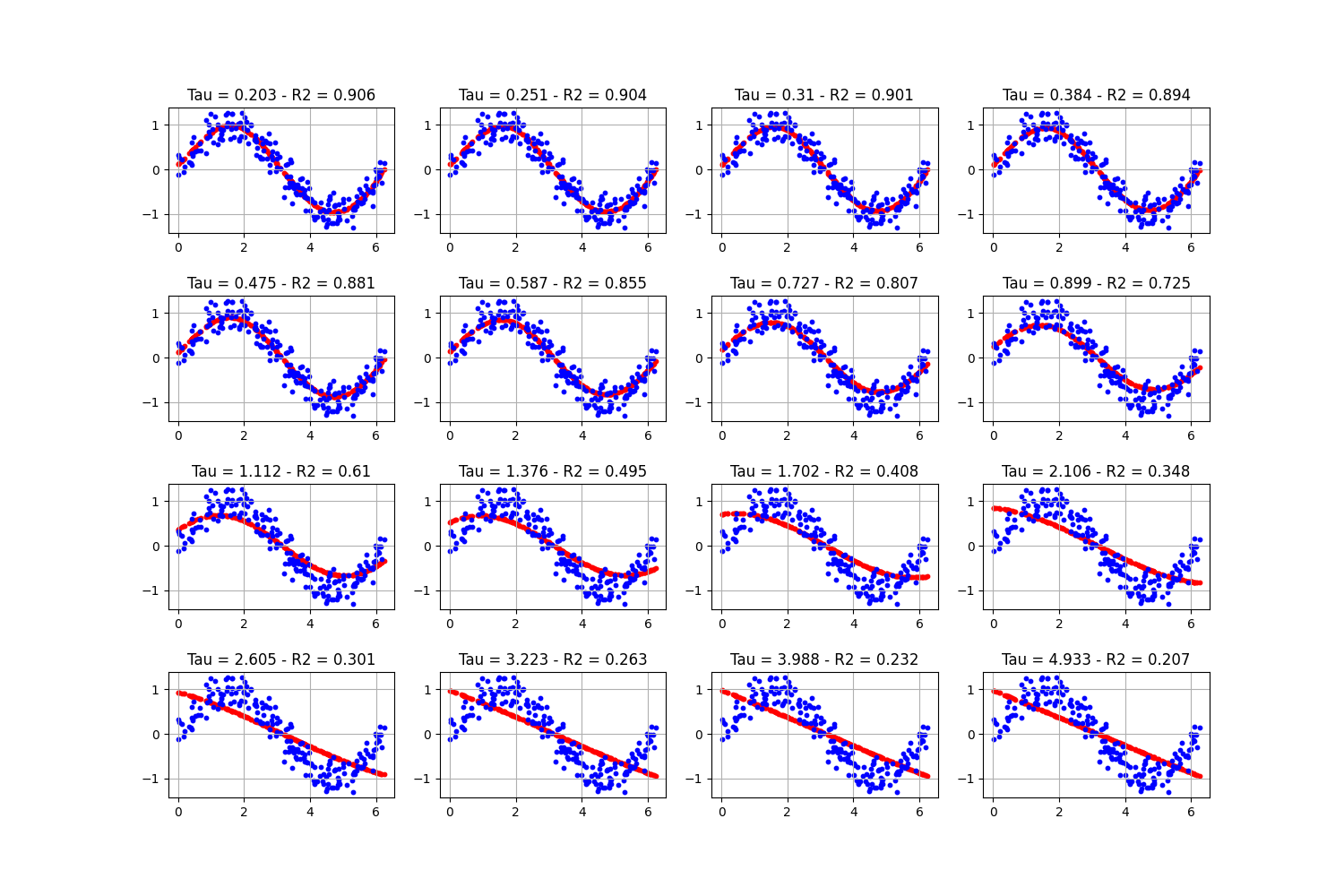
Locally Weighted Regression on a Sine Function
This script demonstrates Locally Weighted Regression (LWR), using a Gaussian kernel to assign weights to training samples based on their distance from a test point.
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from DLL.MachineLearning.SupervisedLearning.LinearModels import LinearRegression
from DLL.Data.Metrics import r2_score
from DLL.Data.Preprocessing import data_split
X = torch.linspace(0, 2 * torch.pi, 1000).unsqueeze(1)
y = torch.sin(X).squeeze() + 0.2 * torch.randn_like(X.squeeze())
X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test, _, _ = data_split(X, y)
def get_weight(train, test, tau):
d2 = torch.sum((train - test) ** 2, dim=1)
w = torch.exp(-d2 / (2. * tau * tau))
return w
def get_pred(tau):
y_pred = []
for test_point in X_test:
weight = get_weight(X_train, test_point, tau)
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train, sample_weight=weight)
y_pred.append(model.predict(test_point.reshape(1, -1))[0])
y_pred = torch.stack(y_pred).reshape(-1,)
return y_pred
n = 4
m = 4
fig, axes = plt.subplots(m, n, figsize=(15, 10))
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5)
axes = axes.ravel()
taus = torch.logspace(torch.log(torch.Tensor([0.5]).squeeze()), torch.log(torch.Tensor([2.0]).squeeze()), m * n)
for i, ax in enumerate(axes):
y_pred = get_pred(taus[i])
ax.set_title(f"Tau = {round(taus[i].item(), 3)} - R2 = {round(r2_score(y_test, y_pred), 3)}")
ax.scatter(X_test, y_pred, s=10, c="r", label="prediction")
ax.scatter(X_test, y_test, s=10, c="b", label="true")
ax.grid()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 9.062 seconds)